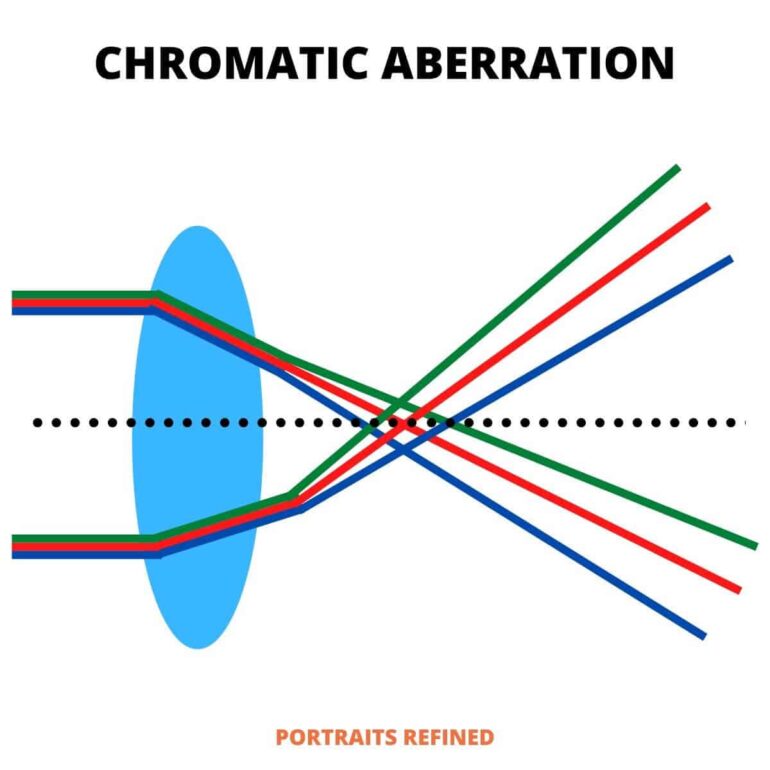
Have you ever noticed a strange purple or green fringing in your video footage? If so, you have likely experienced a phenomenon known as chromatic aberration. Chromatic aberration is an optical effect caused by a lens’ inability to focus all colors of light onto the same plane. This effect can be very distracting, reducing the overall quality of your footage.
But what exactly causes chromatic aberration in video? In order to answer this question, we must first understand how lenses work and how they bend light. Light is composed of multiple colors and each color has a different wavelength. When light passes through a lens, the lens refracts each wavelength differently, resulting in the colors being focused at different points. This is what causes chromatic aberration. The lens is unable to focus all colors of light onto the same plane, resulting in a halo of color around the edges of objects.
Chromatic aberration can be caused by a variety of factors, such as lens imperfections, the quality of the lens, and the angle at which the light enters the lens. Additionally, the effect is more pronounced when using a wide-angle lens or when shooting at a wider aperture setting. When chromatic aberration occurs, it not only reduces the quality of your footage, but it can also create a distraction for the viewer.
In this blog post, we will explore the causes of chromatic aberration in video and discuss how it can be avoided or corrected. We will also discuss how to compensate for chromatic aberration in post-production and provide an example of what chromatic aberration looks like in video footage. So, if you want to learn more about chromatic aberration and how to prevent it in your own video projects, keep reading.
What causes chromatic aberration in video?
Chromatic aberration, or “color fringing”, is a common issue in video production. It occurs when light passes through a camera lens and is bent incorrectly, resulting in different colors being separated. This can cause an array of issues in your video, from blurry edges to bright colors with jagged edges.
Understanding what causes chromatic aberration is key to avoiding it and ensuring that your videos look their best. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes of chromatic aberration, and how you can prevent it from ruining your videos.
What is Chromatic Aberration?
Chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon that occurs when light of different colors passes through a lens and is bent differently. This results in different colors being separated and causing a visible blur or fringe on the edges of an image or video.
The most common type of chromatic aberration is known as longitudinal chromatic aberration, or “longitudinal CA”. This is when light of different colors passes through the lens and is bent at different angles, resulting in the colors being separated. This can cause the edges of an image to appear blurry or distorted.
What causes Chromatic Aberration?
Chromatic aberration occurs because the lens of your camera is virtually a prism. As light passes through the prism, the light is bent and the color wavelengths become separated. Lens imperfections can cause the light to bend incorrectly, and certain wavelengths to change their speed or angle.
The most common cause of chromatic aberration is lens aberrations, which are imperfections in the lens that can cause light to be bent in different directions. These aberrations can be caused by poor lens design, poor lens construction, or the use of cheaper lenses.
Other causes of chromatic aberration include the use of too much contrast or saturation in an image, shooting in low light, and shooting with wide-angle lenses. All of these can cause light to be bent incorrectly, resulting in chromatic aberration.
How to Prevent Chromatic Aberration
The best way to prevent chromatic aberration is to use lenses that are designed to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration. There are lenses available that are specifically designed to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration, and these are generally more expensive than regular lenses.
You can also reduce chromatic aberration by using post-processing techniques such as sharpening, contrast reduction, and lens correction. These techniques can help to reduce the visibility of chromatic aberration and improve the overall quality of your videos.
Finally, you can also reduce chromatic aberration by shooting in higher light levels, avoiding high contrast shots, and using telephoto lenses instead of wide-angle lenses.
Chromatic aberration is a common issue in video production, and it can be caused by a variety of factors. The most common cause is lens aberrations, which are imperfections in the lens that can cause light to be bent in different directions. To prevent chromatic aberration, use lenses that are designed to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration, use post-processing techniques, and shoot in higher light levels. By following these tips, you can ensure that your videos are free of chromatic aberration and look their best.
What is chromatic aberration how it can be removed?
Chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon that occurs when a lens fails to focus all colors of light on the same plane or focal point. It is a common problem in photography and is most common when using a wide-angle lens. Chromatic aberration can cause images to appear blurry and out of focus, with colors appearing fringed or distorted. Fortunately, there are a few ways to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration in your images.
What Causes Chromatic Aberration?
Chromatic aberration is caused by the fact that different colors of light travel at different speeds through a lens. When a lens fails to focus all colors of light on the same focal point, it causes chromatic aberration. This is because the lens is unable to bend the colored rays of light equally.
How Can Chromatic Aberration Be Removed?
The most effective way to remove chromatic aberration is to use an achromatic doublet or achromatic triplet. An achromatic doublet is a two-element lens consisting of two pieces of glass with different refractive indices. The two elements work together to reduce chromatic aberration by focusing the different colors of light to the same focal point.
An achromatic triplet, on the other hand, is a three-element lens that has three pieces of glass with different refractive indices. This lens is more effective at reducing chromatic aberration because it splits the colors of light into three separate components and focuses them to the same focal point.
Another way to reduce chromatic aberration is to use software. Many image editing programs can be used to reduce chromatic aberration. These programs can detect and correct areas of the image that have been affected by chromatic aberration.
Tips for Reducing Chromatic Aberration
There are a few tips for reducing chromatic aberration in your images. First, try to avoid using wide-angle lenses when shooting. Wide-angle lenses are more prone to chromatic aberration than longer focal length lenses.
Second, use a lens that has been designed specifically to reduce chromatic aberration. These lenses are usually labeled as “low dispersion” or “ED” lenses.
Third, use a lens hood when shooting. Lens hoods can help to reduce the amount of light that enters the lens and can help to reduce chromatic aberration.
Finally, use a high-quality tripod when shooting. The use of a tripod can help to reduce camera shake, which can lead to blurred images and chromatic aberration.
Chromatic aberration is a common problem in photography and can cause images to appear blurry and out of focus. Fortunately, there are a few ways to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration in your images. By using an achromatic doublet or triplet lens, using software to correct chromatic aberration, avoiding wide-angle lenses, using a lens hood, and using a high-quality tripod, you can improve the quality of your images and reduce chromatic aberration.
How do you compensate chromatic aberration?
Chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon that occurs when a lens fails to focus all wavelengths of light to the same point. As a result, some colors may appear blurred or out-of-focus. It is especially common in long lenses and in low-quality optics. Fortunately, chromatic aberration can be compensated for with the proper lens and camera settings.
Chromatic aberration occurs when different wavelengths of light pass through a single lens at different points. This causes the image to appear blurry or distorted. The most common type of chromatic aberration is axial chromatic aberration, which is caused by the refractive index of the lens material varying with wavelength. It produces a fringing of different colors around the edges of an object, which is especially noticeable when there is a high contrast between the object and the background.
How to Compensate Chromatic Aberration
The best way to reduce or even compensate chromatic aberration is to store the chromatic aberration characteristics of the lens regarding zoom ratio, aperture and focal distance to the camera recorder beforehand. This allows the camera to automatically adjust for the aberration when shooting.
When using digital imaging systems, it is possible to adjust the chromatic aberration correction in software. Many digital editing programs have built-in chromatic aberration correction tools that allow you to manually adjust the settings to reduce the effect of the aberration.
Optimizing for Chromatic Aberration
To minimize the effects of chromatic aberration, use lenses with quality optics and high-quality glass elements. Quality optics will help reduce the amount of light that is scattered and refracted, resulting in less aberration. Additionally, lenses with higher quality glass elements will also help reduce chromatic aberration.
Another way to optimize for chromatic aberration is to use a shorter focal length and wider angle lenses. This will help minimize the amount of light that is scattered and refracted and will help reduce the incidence of chromatic aberration.
Conclusion
Chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon that can cause a variety of color distortions. Fortunately, it is possible to reduce or even compensate for chromatic aberration with the proper lens and camera settings. By storing the chromatic aberration characteristics of the lens, using quality optics and high-quality glass elements, and using a shorter focal length and wider angle lenses, you can minimize the effects of chromatic aberration and ensure the highest quality images.
What is chromatic aberration and why does it occur?
Chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon that occurs when a lens is unable to properly refract all the wavelengths of colour in the same point. It’s a common issue in photography that affects almost all lenses, though high-quality lenses will present with less chromatic aberration than lower-quality ones. In this article, we’ll explain what chromatic aberration is, why it occurs, and how you can avoid it in your photography.
Chromatic aberration is an optical defect that causes different colours of light to focus at different points in an image. This results in an unwanted ‘fringing’ effect that can be seen along edges and boundaries in an image. Chromatic aberration can be seen in both digital and film photography, and it can range from minor to severe depending on the lens quality and exposure settings.
Types of Chromatic Aberration
There are two main types of chromatic aberration: axial and lateral. Axial chromatic aberration occurs when different colours of light focus at different distances from the lens, and it is usually seen as a colour fringing around edges. Lateral chromatic aberration, on the other hand, occurs when different colours of light focus at different points on the sensor, and it is usually seen as a colour fringing in the middle of an image.
Why Does Chromatic Aberration Occur?
Chromatic aberration occurs because lenses are not perfect. Light is composed of different colours, and each colour has a different refractive index. When light passes through a lens, it is bent and refracted in different directions. However, different colours of light have a different refractive index, and this means that each colour will be bent and refracted differently. As a result, the different colours of light will focus at different points, which causes the chromatic aberration.
How to Avoid Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic aberration can be avoided by using high-quality lenses and choosing the right exposure settings. Higher-quality lenses are better at refracting different colours of light in the same direction, which reduces the amount of chromatic aberration. Additionally, using a small aperture can help reduce chromatic aberration, as it reduces the amount of light that passes through the lens. Finally, using a lens hood can also help reduce chromatic aberration, as it shields the lens from stray light that can cause colour fringing.
Chromatic aberration is an optical defect that occurs when a lens is unable to properly refract all the wavelengths of colour in the same point. It’s a common issue in photography that affects almost all lenses, though high-quality lenses will present with less chromatic aberration than lower-quality ones. Fortunately, there are a few simple steps you can take to avoid chromatic aberration, such as using a high-quality lens and choosing the right exposure settings. By following these tips, you can ensure that your images are free of chromatic aberration.
What are the two types of chromatic aberration?
Chromatic aberration is a common optical phenomenon that occurs when light passes through a lens and is refracted at different angles for different wavelengths of light, resulting in a blurred or distorted image. It is caused by the fact that different colors of light travel at different speeds and are refracted by different amounts when passing through a lens. This phenomenon can significantly reduce the quality of an image, making it difficult to distinguish between objects and colors. To prevent or reduce chromatic aberration, it’s important to understand the two types of chromatic aberration and how to correct them.
Axial Chromatic Aberration
Axial chromatic aberration, sometimes referred to as longitudinal chromatic aberration, is the most common type of chromatic aberration. It occurs when different wavelengths of light are focused at different distances from the lens. This causes different colors to focus at different points, resulting in a blurred or distorted image. Axial chromatic aberration can be corrected by using achromatic lenses, which are designed to reduce or eliminate axial chromatic aberration.
Lateral Chromatic Aberration
Lateral chromatic aberration, also known as transverse chromatic aberration, occurs when different wavelengths of light are focused at different positions in the image plane. This type of chromatic aberration results in different colors being focused at different points, resulting in a blurred or distorted image. Lateral chromatic aberration can be corrected by using an apochromatic lens, which is designed to reduce or eliminate lateral chromatic aberration.
Preventing Chromatic Aberration
The best way to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration is to use lenses that are designed specifically to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration. Achromatic lenses are designed to reduce or eliminate axial chromatic aberration, while apochromatic lenses are designed to reduce or eliminate lateral chromatic aberration. In addition, many lenses come with additional features such as special coatings or lens elements that are designed to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration.
Correcting Chromatic Aberration
If chromatic aberration is already present in an image, there are several ways to correct it. Some image editing software programs include tools that can be used to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration. In addition, many image processing programs allow you to adjust the levels and curves of the image to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration. Finally, some lenses come with special coatings or lens elements that can be used to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration.
Chromatic aberration is a common optical phenomenon that can significantly reduce the quality of an image. The best way to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration is to use lenses that are designed specifically to reduce or eliminate chromatic aberration. In addition, there are several methods of correcting chromatic aberration, including using image editing software and adjusting the levels and curves of the image. By understanding the two types of chromatic aberration and how to correct them, you can ensure that your images are clear and free of distortion.
What is an example of chromatic aberration?
Chromatic aberration is a common optical problem that occurs when light rays pass through a lens, causing the image to be distorted. It is caused by the refraction of light of different wavelengths, which results in a fringing or halo effect around objects in an image. This halo is usually seen as a color fringe around the edges of the object and is most commonly seen as red, green, or blue in color.
Chromatic aberration can be a major issue for photographers, especially those working with digital cameras. This is especially true for lenses with longitudinal chromatic aberration problems, which can cause fringing around objects in the image, even in the center. Red, green, blue or a combination of these colors can appear around objects, and this can be very difficult to correct in post-processing.
What is Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration?
Longitudinal chromatic aberration, also known as axial chromatic aberration, is an optical aberration caused by the variation in the refractive index of a lens with different wavelengths of light. The refractive index of a lens is a measure of the speed at which light passes through the lens, and it is different for each wavelength of light.
In lenses with longitudinal chromatic aberration, the refractive index of the lens is not constant across the entire spectrum of light. This results in different wavelengths of light being focused at different points, which in turn causes a fringing or halo effect around objects in the image.
How Can Longitudinal Chromatic Aberration Be Reduced?
Fortunately, longitudinal chromatic aberration can be dramatically reduced by stopping down the lens. Stopping down a lens refers to reducing the size of the lens opening, which allows less light to pass through the lens and reduces the amount of chromatic aberration.
Another way to reduce chromatic aberration is to use a different type of lens, such as an apochromatic lens. Apochromatic lenses are designed to minimize chromatic aberration, and they typically have three or more elements that are specially designed to reduce chromatic aberration.
Chromatic aberration is a common optical problem that can have a major impact on the quality of an image. Longitudinal chromatic aberration is caused by the variation in the refractive index of a lens with different wavelengths of light, and it can be a major issue for photographers. Fortunately, this type of chromatic aberration can be dramatically reduced by stopping down the lens or using an apochromatic lens.
In conclusion, chromatic aberration is an optical phenomenon caused by lens imperfections. Light passes through the prism of the lens and is bent, causing different color wavelengths to separate and cause a variety of problems with your video. This can lead to fringing along the edges of objects, color shifting, and halos around objects in your video. While some of these effects can be desirable, often times they can be a nuisance. Luckily, there are a few ways to reduce chromatic aberration, such as using a better quality lens, using a filter, or even using special software to remove the effects. With the right tools and know-how, you can ensure that your videos come out looking their best.